Study Notes
Overview
Welcome to your deep dive into the 'Problems of Growth', a fundamental topic in the WJEC GCSE Business specification. While business growth is often seen as a primary objective, examiners expect candidates to adopt a critical perspective, understanding that expansion brings significant risks. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to analyse these problems, focusing on two core areas: internal diseconomies of scale and the financial trap of overtrading. We will explore how communication falters, coordination breaks down, and motivation suffers as a firm gets bigger. You will also learn to dissect the perilous cash flow implications of rapid growth. By mastering these concepts and the specific language examiners look for, you will be able to move beyond simple descriptions and provide the nuanced analysis required for the highest grades.
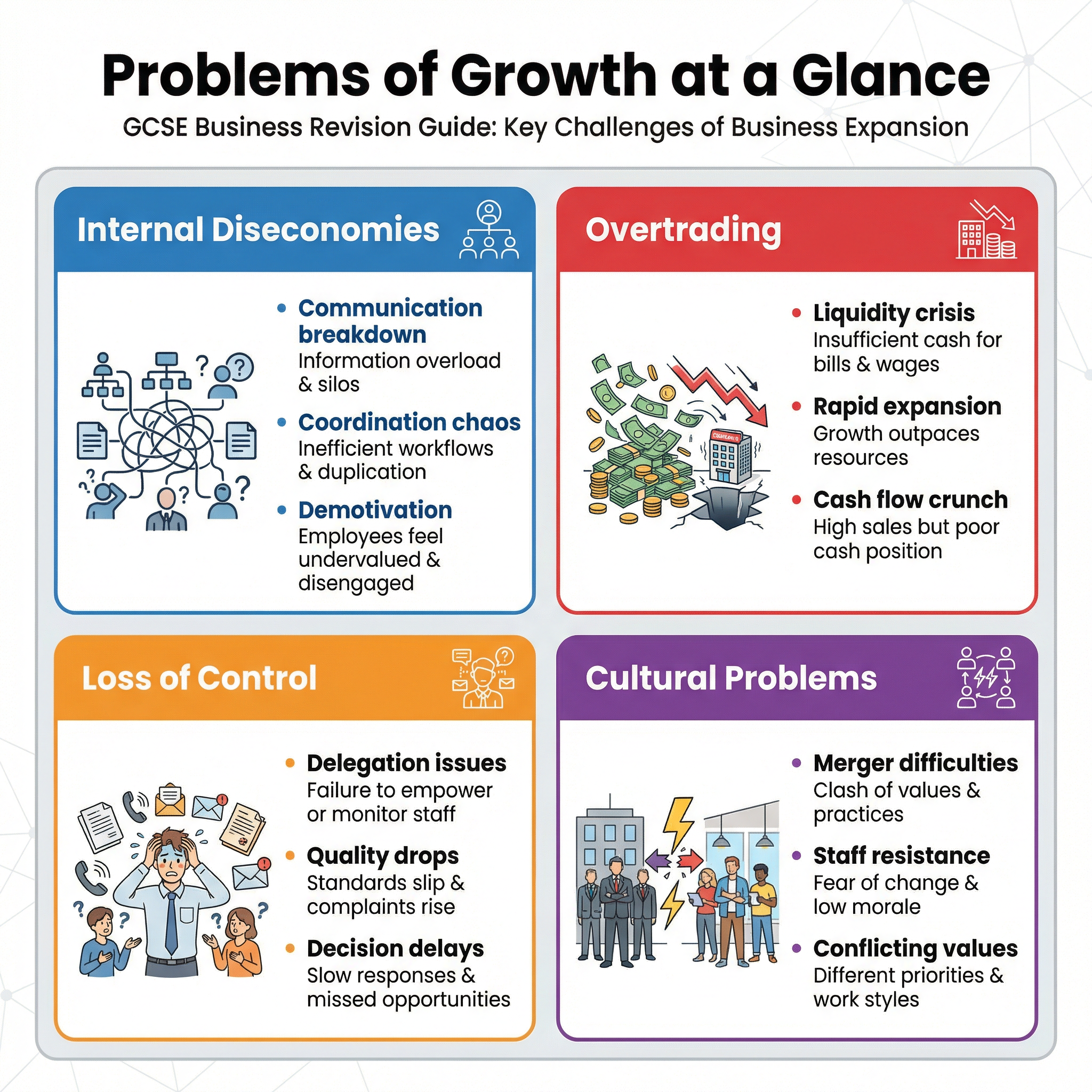
Key Problems of Growth
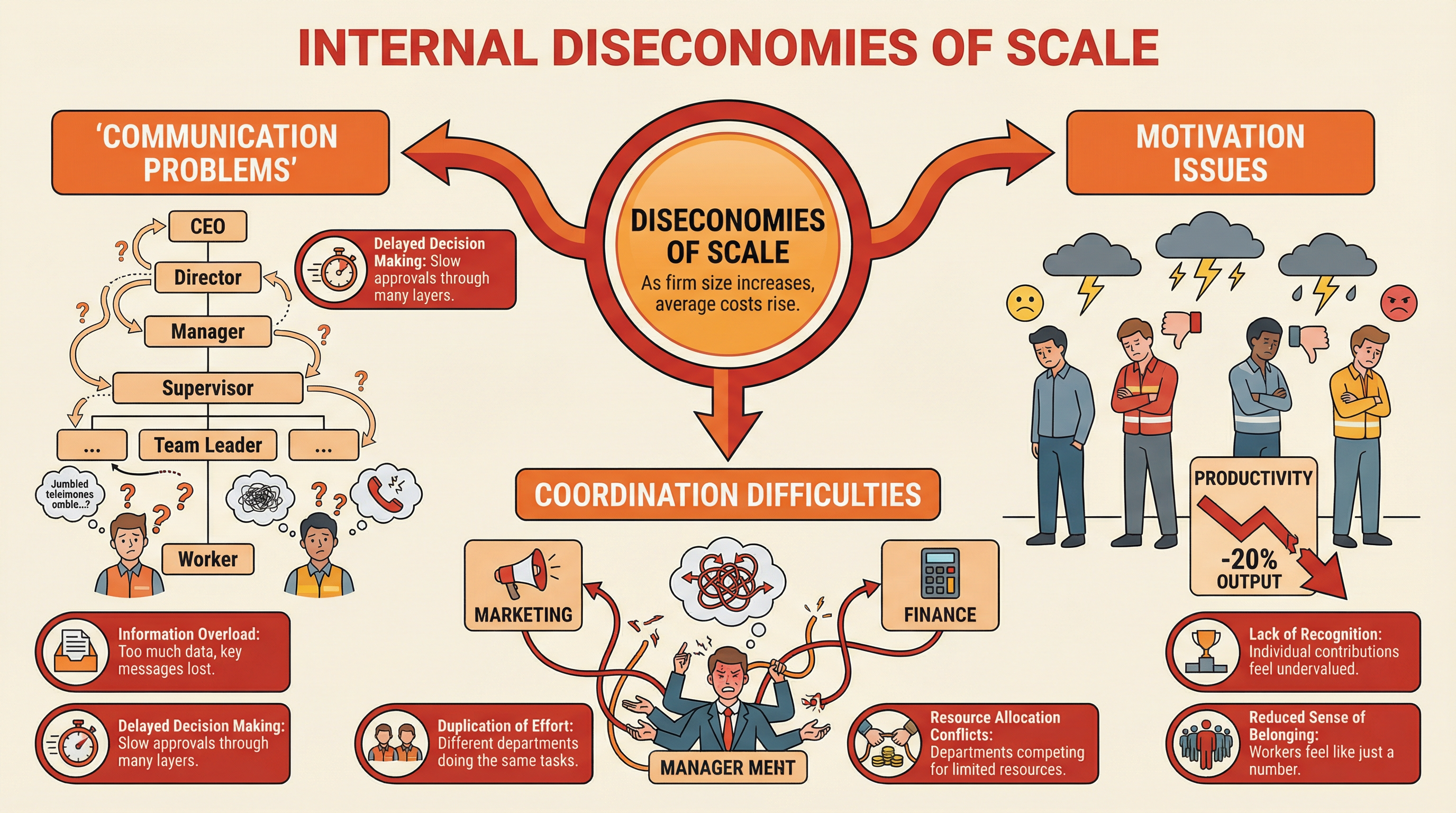
Internal Diseconomies of Scale
What it is: This occurs when a business grows so large that its average cost per unit starts to increase. It's the opposite of the much more friendly 'economies of scale'. This happens not because of external factors like rising raw material prices, but because of internal inefficiencies that creep in as the organisation becomes more complex.
Why it matters: For the exam, you must explain the causes of diseconomies of scale. Credit is given for identifying the specific mechanisms that lead to this inefficiency. Simply stating 'costs go up' is not enough.
Specific Knowledge: The three key causes to remember are:
- Communication Problems: In a small firm, communication is fast and direct. In a large firm with a tall organisational structure and a long chain of command, messages can be slow, distorted, or lost entirely. This leads to poor decision-making and a disconnect between senior management and employees on the ground.
- Coordination Difficulties: As a business grows, it develops specialised departments (e.g., marketing, finance, operations). If these departments are not effectively coordinated, they can work against each other. For example, marketing might launch a product promotion that operations cannot supply, leading to customer dissatisfaction and wasted resources.
- Motivation Issues: In a large, impersonal organisation, individual employees can feel like a small, insignificant 'cog in a machine'. This sense of alienation can lead to a decline in morale, lower productivity, and an increase in staff turnover, all of which increase costs.
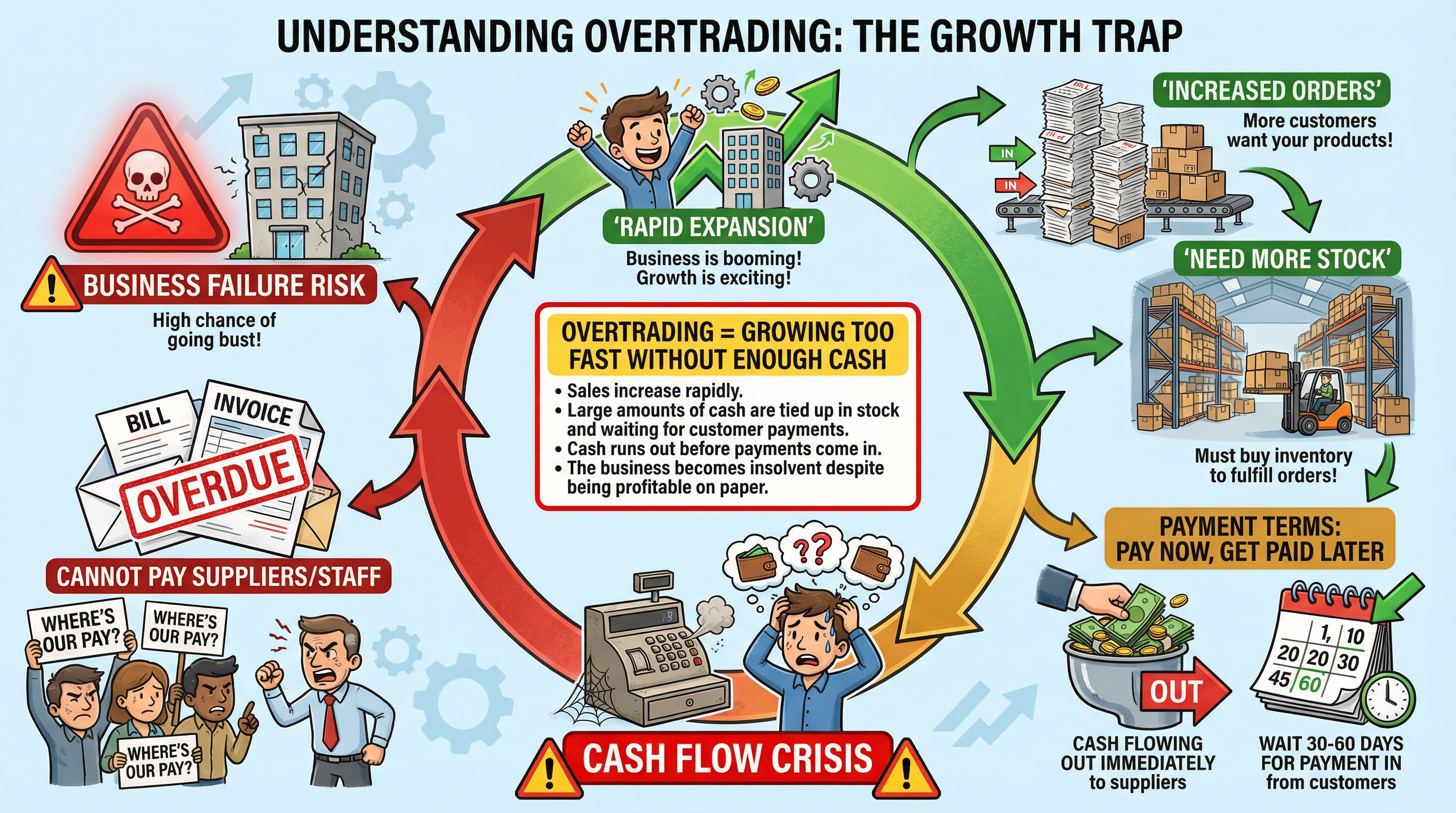
Overtrading
What it is: Overtrading is a serious financial problem that occurs when a business expands too quickly without having sufficient working capital to support the increased volume of sales. It's a cash flow crisis, not a profitability crisis.
Why it matters: This is a high-level concept that can really differentiate your answer. Candidates who can accurately explain overtrading demonstrate a strong grasp of business finance. The key is to distinguish between profit and cash.
Specific Knowledge: The typical scenario is as follows:
- A business secures a large order from a new customer.
- To fulfil this order, it must immediately pay for raw materials, labour, and other expenses.
- However, the customer may have a long credit period (e.g., 60-90 days) before they pay their invoice.
- During this period, the business has a severe shortage of cash (a liquidity problem) and may be unable to pay its own suppliers, staff, or rent, even though it is technically profitable on paper. This can lead to business failure.
Second-Order Concepts
Causation
- Short-term causes: A sudden large order, the decision to open multiple new locations at once, a merger with another business.
- Long-term causes: A sustained period of aggressive growth, a management culture focused only on sales figures without considering operational capacity, a failure to secure long-term financing to support expansion.
Consequence
- Immediate effects: Cash flow shortages, missed supplier payments, decline in product/service quality, stressed and demotivated employees.
- Long-term effects: Damage to brand reputation, loss of key staff, business failure (insolvency), loss of market share to more sustainably managed competitors.
Change & Continuity
- Change: The business moves from a simple, flat structure to a complex, hierarchical one. The culture may change from a close-knit 'family feel' to an impersonal corporate environment. Decision-making changes from being fast and centralised to slow and bureaucratic.
- Continuity: The core mission of the business might remain the same, but its ability to deliver on that mission is compromised. The business may continuously be trying to 'catch up' with its own growth.
Significance
- The problems of growth are significant because they demonstrate that business objectives can conflict. The pursuit of growth can directly undermine profitability and even survival. It highlights the critical importance of financial planning and effective management in ensuring long-term business success.