Study Notes

Overview
Welcome to your deep dive into the art of economic evaluation, a cornerstone of the OCR J205 GCSE Economics specification. Accounting for 30% of your final grade, mastering Assessment Objective 3 (AO3) is not just an advantage; it is essential for achieving a high pass. This study guide is designed to demystify the process, transforming you from a candidate who can simply state economic theory (AO1) and apply it (AO2) into one who can critically analyse, weigh arguments, and form substantiated judgements. Examiners are looking for a logical thought process, where you can confidently explore both the positive and negative implications of an economic decision, policy, or event. You will learn to construct developed chains of reasoning, use the provided case study material to its full potential, and deploy key evaluative phrases that signal to the examiner you are operating at the highest level. This is your playbook for turning good answers into great ones.
The Core of Evaluation: Building a Balanced Argument
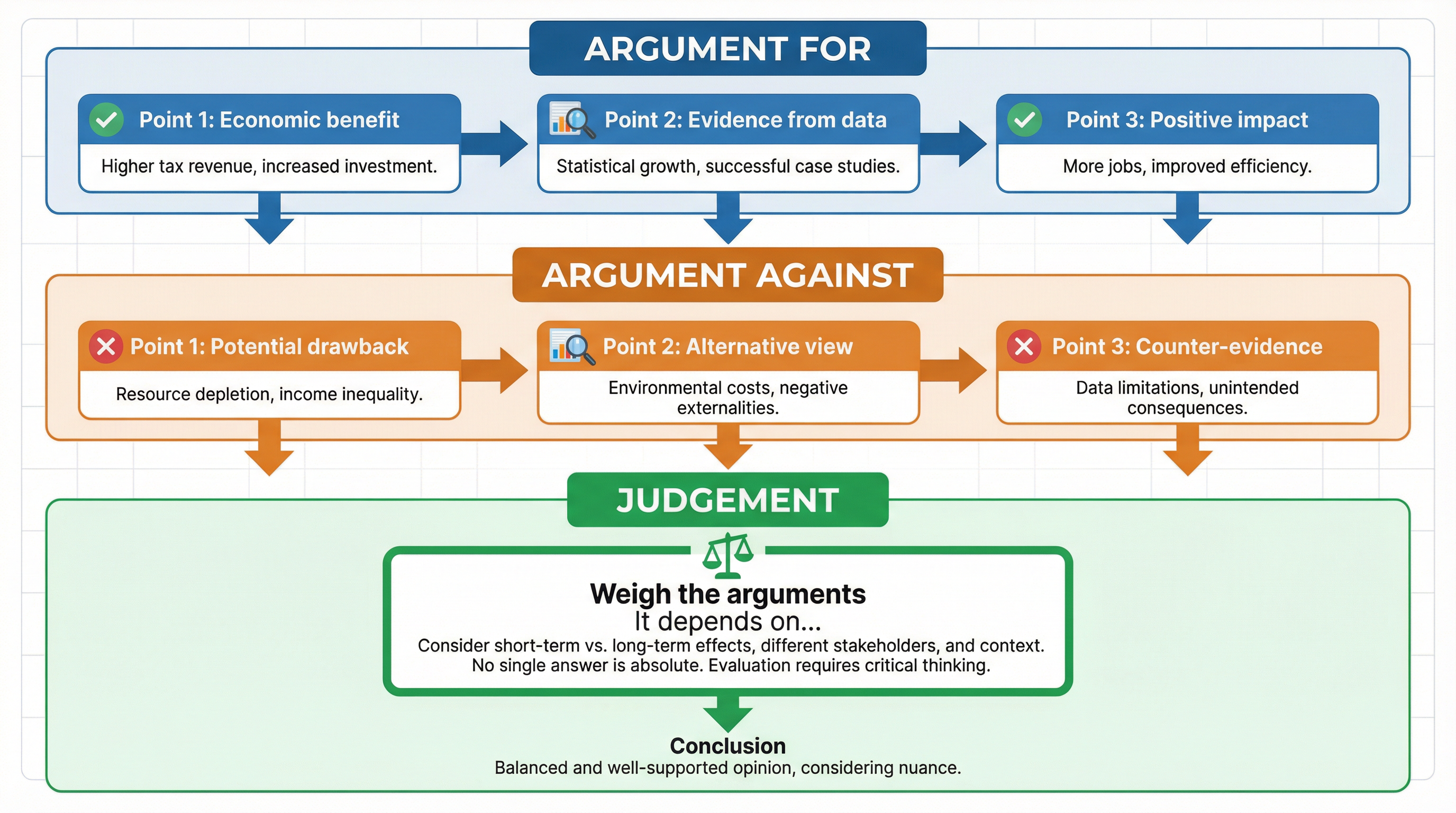
At its heart, evaluation is about balance. For any question using command words like "evaluate", "assess", or "to what extent", a one-sided answer will automatically be capped at Level 2. To access the top mark bands, candidates must demonstrate the ability to consider multiple perspectives. This involves presenting a coherent argument for a particular viewpoint, and then providing a similarly well-developed counter-argument.
Key Principle: Every economic action has costs and benefits, winners and losers, and intended and unintended consequences. Your job is to explore this complexity.
Developing Chains of Reasoning
A simple assertion (e.g., "This will increase unemployment") will earn minimal credit. To score highly, you must build a chain of reasoning that explains the economic mechanism at play. Use connective phrases to link your points logically:
- "This leads to...": Shows a direct consequence.
- "Which means that...": Explains the implication of the previous point.
- "Therefore...": Introduces the logical conclusion of the chain.
Example Chain: An increase in the National Minimum Wage (Point) leads to higher wage costs for firms (Explanation). This means that firms may reduce their demand for labour to protect their profit margins (Further Explanation), therefore causing a rise in structural unemployment, particularly in low-skilled sectors (Link to Question).
The Power of "It Depends On..."
The most effective evaluative tool is the phrase "It depends on...". This demonstrates to the examiner that you understand that economic principles are not absolute and their effects are contingent on various factors. A strong conclusion will always weigh the arguments and use one of these contextual factors to make a final judgement.
Key Evaluative Contexts to Consider:
- Magnitude: How large is the change? A 1% increase in a tax will have a vastly different impact than a 50% increase.
- Time: What are the short-run versus the long-run effects? A policy might be beneficial in the short run but have negative long-term consequences.
- Elasticity: The price elasticity of demand (PED) and supply (PES) are critical. For example, the effectiveness of an indirect tax depends heavily on whether demand for the good is elastic or inelastic.
- Stakeholders: Who is affected? Consider the impact on consumers, producers, the government, and the wider society (externalities).
- Starting Point: What is the current state of the economy? A policy's impact will differ if the economy is in a recession versus a boom.
Using the Data: Securing Application Marks (AO2)
Evaluation (AO3) is intrinsically linked to application (AO2). The case study or insert provided in the exam is not just background reading; it is a resource you must actively use to support your arguments. Quoting specific data points, figures, or contextual details is the only way to secure AO2 marks.
- Weak Statement: "The business has seen its revenue fall."
- Strong Statement (with AO2): "As stated in the insert, the business has seen its revenue fall by 15% from £5.2 million to £4.42 million between 2022 and 2023, indicating a significant decline in sales."
Always be explicit. Use phrases like "According to the data..." or "The case study highlights that..." to signpost your use of the provided material.
